How Reverse Osmosis Works
Ever wanted to know how Reverse Osmosis Works?
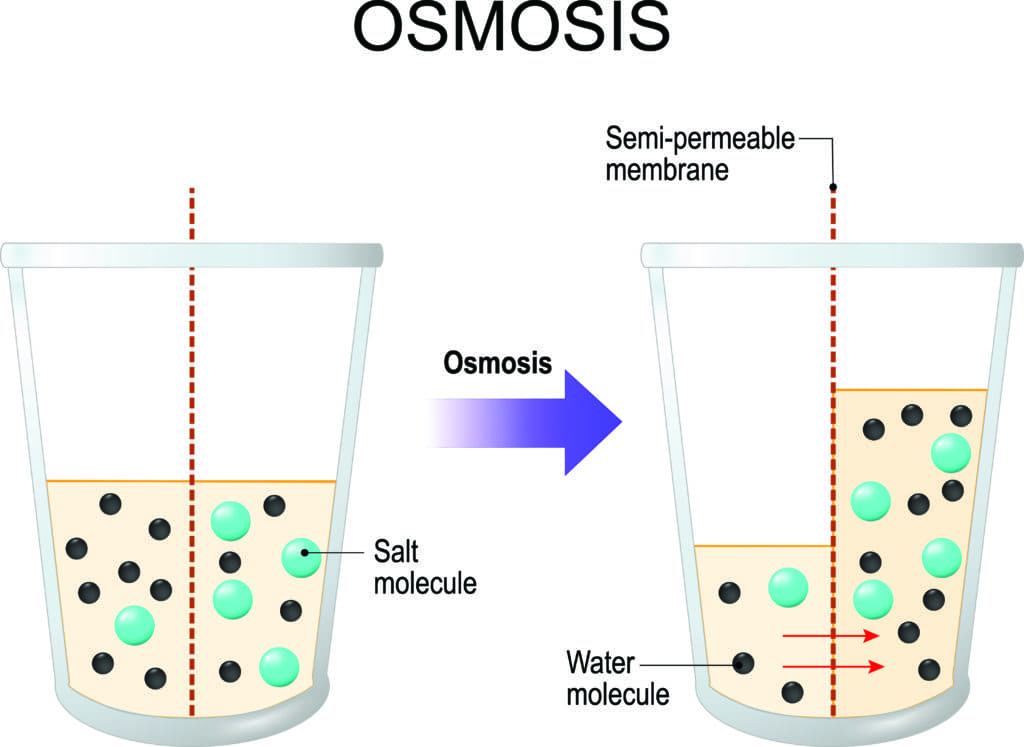
Osmosis is a natural process in which a solvent (e.g. water) moves from an area of low solute concentration through a membrane to an area of high solute concentration. This movement of solvent aims to equalise the solute concentration on both sides of the membrane.
To understand the purpose and process of Reverse Osmosis you must first understand the naturally occurring process of Osmosis.
Osmosis is a naturally occurring phenomenon and one of the most important processes in nature. It is a process where a weaker saline solution will tend to migrate to a strong saline solution. Examples of osmosis are when plant roots absorb water from the soil and our kidneys absorb water from our blood.
Here is a diagram which shows how osmosis works. A solution that is less concentrated will have a natural tendency to migrate to a solution with a higher concentration. For example, if you had a container full of water with a low salt concentration and another container full of water with a high salt concentration and they were separated by a semi-permeable membrane, then the water with the lower salt concentration would begin to migrate towards the water container with the higher salt concentration.
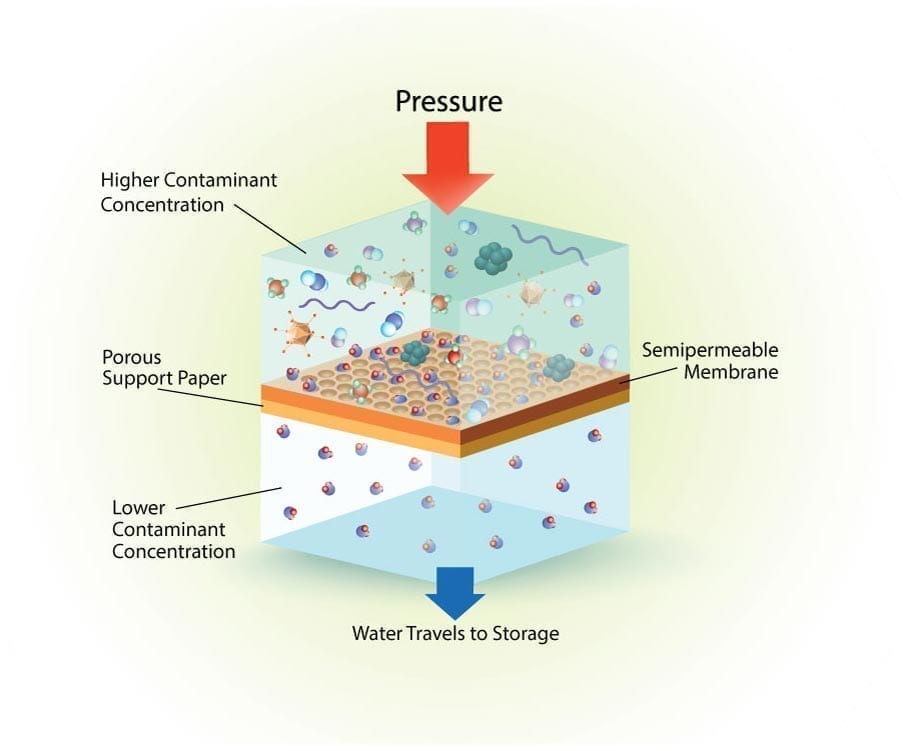
Reverse Osmosis is the process of Osmosis in reverse. Whereas Osmosis occurs naturally without energy required, to reverse the process of osmosis you need to apply energy to the more saline solution. A reverse osmosis membrane is a semi-permeable membrane that allows the passage of water molecules but not the majority of dissolved salts, organics, bacteria and pyrogens. However, you need to ‘push’ the water through the reverse osmosis membrane by applying pressure that is greater than the naturally occurring osmotic pressure in order to desalinate (demineralize or deionize) water in the process, allowing pure water through while holding back a majority of contaminants.
Here is a diagram outlining the process of Reverse Osmosis. When pressure is applied to the concentrated solution, the water molecules are forced through the semi-permeable membrane and the contaminants are not allowed through.
How Reverse Osmosis Works in the Membrane
Reverse Osmosis works by using a high pressure pump to increase the pressure on the salt side of the RO and force the water across the semi-permeable RO membrane, leaving almost all (around 95% to 99%) of dissolved salts behind in the reject stream. The amount of pressure required depends on the salt concentration of the feed water. The more concentrated the feed water, the more pressure is required to overcome the osmotic pressure.
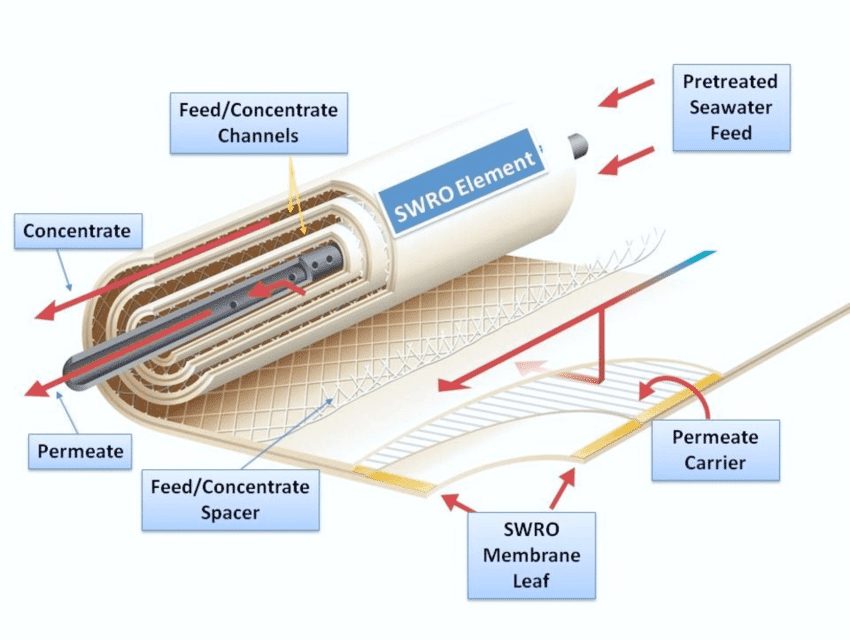
The desalinated water that is demineralized or deionized, is called permeate (or product) water. The water stream that carries the concentrated contaminants that did not pass through the RO membrane is called the reject (or concentrate) stream.
As the feed water enters the RO membrane under pressure (enough pressure to overcome osmotic pressure) the water molecules pass through the semi-permeable membrane and the salts and other contaminants are not allowed to pass and are discharged through the reject stream (also known as the concentrate or brine stream), which goes to drain or can be fed back into the feed water supply in some circumstances to be recycled through the RO system to save water. The water that makes it through the RO membrane is called permeate or product water and usually has around 95% to 99% of the dissolved salts removed from it.
It is important to understand that an RO system employs cross filtration rather than standard filtration where the contaminants are collected within the filter media. With cross filtration, the solution passes through the filter, or crosses the filter, with two outlets: the filtered water goes one way and the contaminated water goes another way. To avoid build up of contaminants, cross flow filtration allows water to sweep away contaminant build up and also allow enough turbulence to keep the membrane surface clean.

Recent Comments